Spotters in "Environment and Health: Air" for CFM & MPH students
Air direction:
1. Wind vane/ Wheather vane/ Wheathercock:
Important points:
- It is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind.
- When the wind is sufficiently strong, the head of the arrow or cockerel indicates the direction from which the wind is blowing.
- The wind vane is placed high enough to avoid wind interference from objects, buildings, and trees like the top of towers, poles, etc.
- Types-Weathervane, Wind Sock, Digital Wind Vane
- Benefits: Safety from storms, very helpful in activities like golf and boat sailing.
Air speed:
2. Anemometer:
Important points:
- It is a device used for measuring wind speed, direction & pressure.
- A common weather station instrument.
- Types- Cup, Vane, Hot-wire, Lesser doppler, Ultrasonic, Pin-pong ball, Plate & Tube anemometer
- Uses: helps indicate a change in weather patterns, such as an approaching storm, which is important for pilots, engineers, and climatologists.
Air/ Atmospheric pressure:
3. Aneroid barometer:

Important points:
- It is an instrument for measuring air pressure as a method that does not involve liquid.
- It uses a small, flexible metal box called an aneroid cell (capsule), which is made from an alloy of beryllium and copper.
- Uses: Common in homes and in recreational boats but also used in meteorology, mostly as barograph and pressure instruments in radiosondes for detecting any changes in the atmospheric pressure.
- More useful in field but requires constant calibration.
4. Mercury barometer:

Important points:
- The mercury barometer's design gives rise to the expression of atmospheric pressure in inches or millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
- It has a vertical glass tube closed at the top sitting in an open mercury-filled basin at the bottom. Mercury in the tube adjusts until the weight of the mercury column balances the atmospheric force exerted on the reservoir.
- It is more accurate than Aneroid barometer.
Air Humidity:
5. Mason's hygrometer:

Important points:
- A standard hygrometer using the wet bulb and dry bulb method to determine air humidity & air temperature.
- Two red liquid-filled thermometers are secured to the plastic scale plates.
- Used at most of the meteorological stations.
6. Sling/ Whirling psychrometer:

Important points:
- It is an instrument that measures the relative humidity and dew point in an area.
- It has two thermometers: a wet bulb and a dry bulb.
- It works on the premise that evaporation is a cooling process. The drier the air, the more evaporation takes place off of the wet bulb, dropping the temperature on the thermometer.
- Uses: For checking humidity level in air-conditioned rooms and installations, to set and check hair hygrometer, in the measurement range of 0 to 100% RH & for measuring wet bulb temperature between 0’C to 180’C.
7. Assman's/ Aspirator psychrometer:
Important points:
- It serves for measuring the air temperature and the humidity.
- Two parallel mounted, equal thermometers with colored petroleum are used.
- The dry bulb thermometer is indicating the true air temperature.
- The difference in temperature of both thermometers results in the psychrometric depression.
- From this, the relative humidity, the dew point temperature, and the vapor pressure of the air may be computed or determined from tables.
8. Electrical hygrometers:
Important points:
- It helps to measure humidity or dewpoint or managing humidity control.
- It measures the change in electrical resistance of a thin layer of lithium chloride, or of a semiconductor device, as the humidity changes.
- Other hygrometers sense changes in weight, volume, or transparency of various substances that react to humidity.
Air pollution:
9. Air quality index:
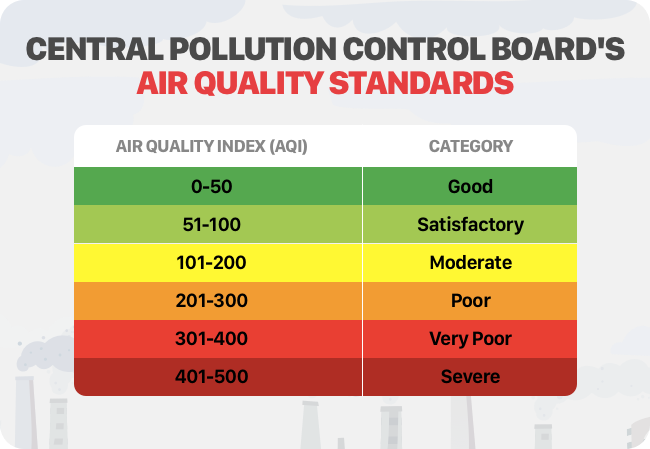
Important points:
- It is an index for reporting air quality on a daily basis.
- It has six categories with the element color scheme which is decided by ambient concentration values of air pollutants & their likely health impacts (breakpoints)
- Objectives- Comparing air quality conditions at different locations/cities, helps in identifying faulty standards and inadequate monitoring programs, helps in analyzing the change in air quality (improvement or degradation) & informs the public about environmental conditions.
References:
- Park, K. (2019). Park's textbook of preventive and social medicine. 25th. Jabalpur, India: M/S Banarsidas Bhanot.
- Kadri AM. (2019). IAPSM's Textbook of Community Medicine. 1st. New Delhi, India: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
- https://www.newconceptlouvers.com/weather-vanes/proud-rooster-weather-vane photo credit
- https://videohive.net/item/wind-gauge-at-the-airport/21162667 photo credit
- https://www.fishersci.com/shop/products/aneroid-barometer/13300176 photo credit
- https://utsic.utoronto.ca/wpm_instrument/mercury-manometer/ photo credit
- https://www.sciencesource.com/archive/Mason-s-Hygrometer-SS2586031.html photo credit
- https://sites.google.com/site/msswcgi/the-inquiry-cycle/step-2-collecting-data/measuring-relative-humidity-sling-psychrometer photo credit
- https://swachhindia.ndtv.com/air-pollution-what-is-air-quality-index-how-is-it-measured-and-its-health-impact-40387/ photo credit
- https://www.eiscolabs.com/products/ph0245s photo credit
- https://www.findel-international.com/product/science/environmental-science/meteorology/mini-anemometer/e8r07120 photo credit
- http://www.extech.com/categories/humidity-meters/ photo credit






Comments
Post a Comment